In the ever-evolving digital landscape, businesses and marketers constantly look for ways to optimize their online presence. One of the most debated topics in search engine optimization (SEO) is whether redirecting a URL affects SEO. Redirects are common for various reasons, such as rebranding, moving content to a new domain, or ensuring website security. Understanding the impact of URL redirection on SEO is crucial for anyone striving to maintain or improve their website’s performance in search engine results. This article delves into the mechanics of URL redirection and examines its effects on SEO.
Defining URL Redirection
Before we proceed, it’s important to understand what URL redirection entails. URL redirection, or URL forwarding, is a technique used to make a web page available under more than one URL. When an internet user tries to access a redirected URL, a page request is sent to the server, sending the user to a different URL. This practice is widely used for various purposes, including maintaining the integrity of broken links, rebranding, or consolidating multiple web pages.
Also Read: When Is 301 Redirect Preferred Over Canonical Link?
Different Types Of Redirects
301 Redirects: Permanent Redirection
A 301 redirect is the most common type of redirect used by webmasters and SEO professionals. This is used when the content of a page has been moved permanently to a new location. It tells search engines that the original URL should be replaced with the new one in their index. This is extremely important for SEO for a number of reasons:
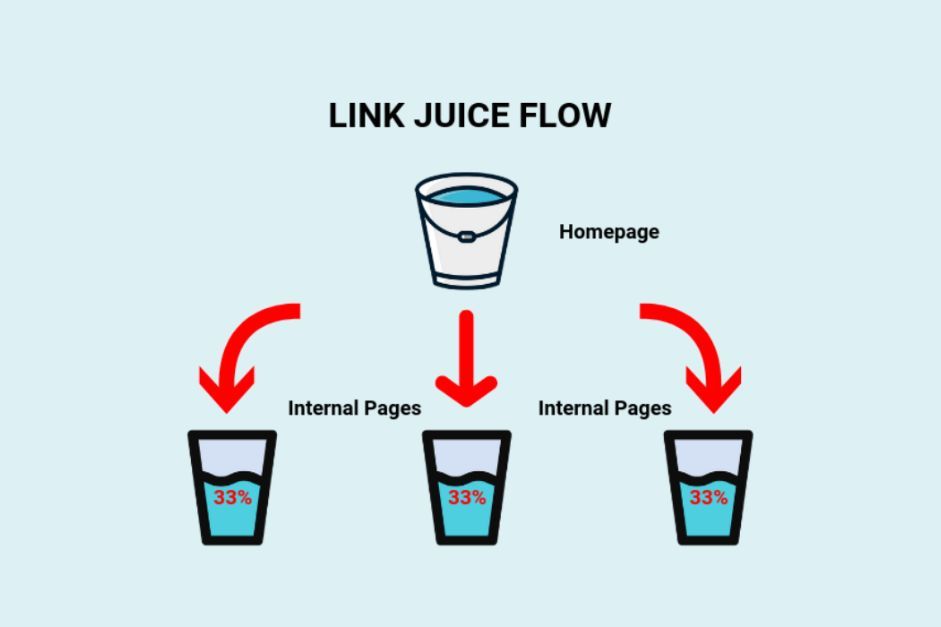
- Link Equity Transfer: A 301 redirect helps transfer most of the link equity from the old URL to the new URL. Link equity, or link juice, is a term used in SEO to describe the value passed from one page to another through hyperlinks. By transferring link equity, a 301 redirect helps preserve the original page’s ranking power.
- Preservation of User Experience: For users who have bookmarked the old URL or find it through an outdated backlink, a 301 redirect ensures that they will be seamlessly taken to the relevant content on the new URL, maintaining a positive user experience.
- Consolidation of Content: In cases where content from multiple pages is merged into a single page, 301 redirects can be used to ensure that the consolidated page retains the SEO value from all the original pages.
302 Redirects: Temporary Redirection
A 302 redirect indicates to search engines that a page has been moved temporarily. This is suitable for situations such as website maintenance, A/B testing, or seasonal promotions. Here are the key aspects of 302 redirects:
- Non-Transfer of Link Equity: Unlike 301 redirects, 302 redirects do not pass the full link equity to the new URL. This is because search engines consider this to be a temporary move and expect the original page to be reinstated in the future.
- Maintaining Original URL in Index: With a 302 redirect, search engines tend to keep the original URL in their index, as they anticipate the content will return to the original URL.
- Use with Caution: It’s important to use 302 redirects judiciously. If used incorrectly in place of a 301 redirect, it can confuse search engines and lead to a loss of ranking for the content.
Also Read: Does 301 Redirect Pass Link Juice?
307 Redirects: An Alternative Temporary Redirection
A 307 redirect is similar to a 302 redirect but is typically used when the content has been moved temporarily, and the HTTP request method (GET, POST) should remain unchanged. It is also seen as a more explicit version of a temporary redirect.

- Preserving HTTP Method: A 307 redirect ensures that the HTTP method does not change. This is particularly important in certain technical scenarios, such as form submissions, where the method and the body of the request should not be altered during the redirect process.
- SEO Considerations: Similar to a 302 redirect, a 307 redirect does not pass full link equity to the new URL, and search engines are likely to retain the original URL in their index.
- Selecting Between 302 and 307: The choice between a 302 and 307 redirect should be based on technical considerations regarding HTTP methods. In terms of SEO, both are treated similarly by search engines.
Meta Refresh
While not an HTTP response, a meta refresh is worth mentioning. It’s client-side redirection and is generally considered less efficient and less SEO-friendly compared to server-side redirects.
The Impact Of Redirects On SEO
Passing Link Equity
One of the most significant factors in understanding the impact of redirects on SEO is the passing of link equity. When using a 301 redirect, a majority of the link equity from the original page is transferred to the new page. However, since 302 or 307 redirects are temporary, not as much link equity is passed on.
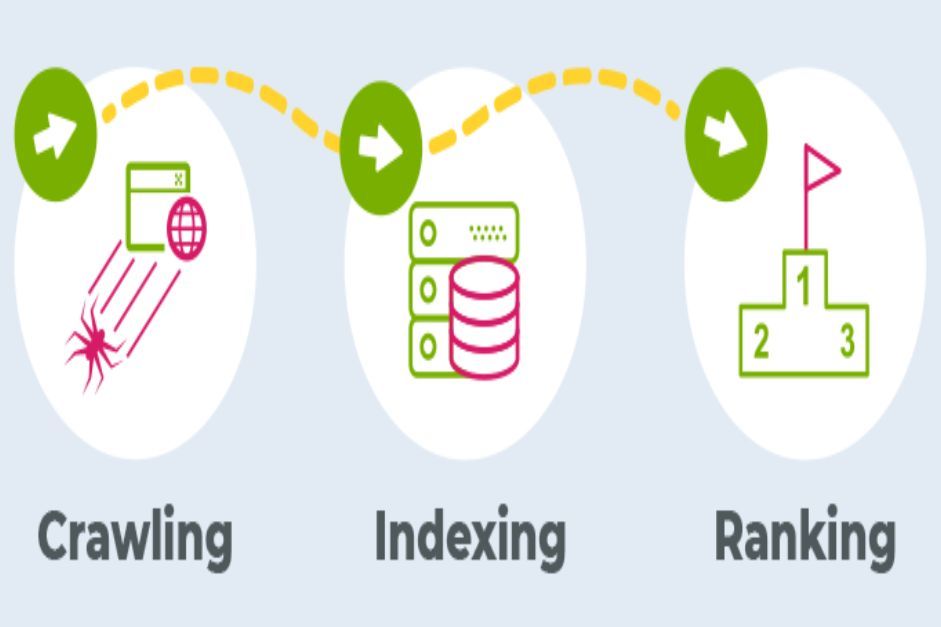
Impact On Crawling And Indexing
The way search engine bots crawl, and index pages is also affected by redirects. A permanent 301 redirect sends a strong signal to search engines that the original URL has been permanently moved. Consequently, search engines will eventually remove the old URL from their index and replace it with the new one. Conversely, in the case of 302 or 307 redirects, search engines may continue to index the original URL while simultaneously indexing the new URL, potentially diluting the value of the content.
Load Time And User Experience
Redirects can add to the load time of a page, which is a known factor in search engine rankings. If a website uses multiple redirects in a chain, it can significantly slow down the page load time, negatively affecting user experience and harming SEO.
Also Read: How To Redirect A URL In WordPress: A Comprehensive Guide
Best Practices For Implementing Redirects

Avoid Redirect Chains
When implementing redirects, it is essential to avoid redirect chains. This means not having a URL redirect to another URL which in turn redirects to another, and so on. It’s best to redirect the original URL directly to the final destination URL.
Use 301 Redirects For Permanent Moves
For permanent moves, always use a 301 redirect to ensure the maximum link equity amount is passed to the new URL. This helps maintain the ranking power of the original page.
Keep An Eye On Page Load Times
Monitoring page load times before and after implementing redirects can help in ensuring that the redirects are not negatively impacting site performance. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights can be used to monitor page load times.
Regularly Audit Redirects
Performing regular audits of the redirects in place is critical. This helps ensure that all redirects are functioning as intended and do not have unintended SEO consequences.
Also Read: Learn How To Redirect A URL To Another URL Free Today!
Conclusion: Redirects Are A Double-Edged Sword
When used correctly, redirecting a URL is a powerful tool that can be instrumental in maintaining and improving a website’s SEO. However, it can have negative consequences if not implemented with caution and understanding. It’s essential to choose the right type of redirect based on the specific scenario and to follow best practices in implementing and monitoring redirects. This will ensure that the integrity and performance of the website are upheld and that SEO benefits are maximized.