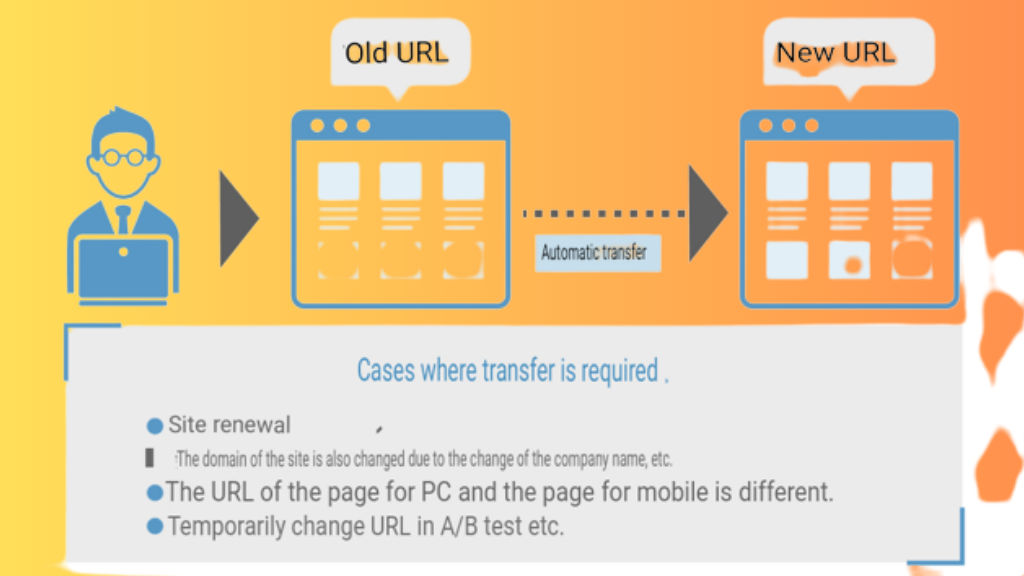
A redirect is a mechanism that automatically forwards from one URL to another. From the SEO point of view, it is recommended not to change the URL as much as possible, but it can be used in the following cases where it is unavoidable to change the URL .
When operating a website, page relocations and URL changes occur frequently.
What you need is a redirect setting.
Redirect settings are a must-do work to maintain Google’s search ranking.
Let’s take a closer look at when to redirect and what an SEO-friendly redirect is.
Why do we need a redirect in the first place?
The purpose is roughly divided into two, usability and SEO perspective .
When changing the domain of the site
When you change your website’s domain, you need to ensure that your old URLs are redirected to your new domain. This is so that even if search engines and users click on the old URL, they will be properly redirected to the new domain.
The most common way to implement redirects is with 301 redirects. A 301 redirect is a process for transitioning URLs, and refers to transitioning to another page. This operation allows you to move to another page while maintaining usability.
However, it’s important to make sure the necessary redirects are in place to move to the new domain. In some cases, this can lead to lower traffic and rankings for your site. Therefore, it is better not to redirect pages that are getting too many hits.

When the page is moved
The most common reason to use redirects is when moving pages (changing URLs).
When you move to another page within the same domain, or when you move to a new domain, you need a redirect to take over the site content and search ranking that you have maintained so far.
The important thing is to make this transition visible to search engines (crawlers).
If search engines don’t recognize this, the new page won’t carry over the previous rankings.
A 301 redirect is necessary in such cases.
A 301 redirect tells search engines about a “permanent transition”.
By transferring the content of the old page and Google’s evaluation to the new page as it is, you can maintain the same evaluation as before even after the page transfer.
Whether you move to a new domain or move pages within the same domain (within your own site), be sure to transfer with a 301 redirect.
The point is that the content before transfer should correspond to the content of the transfer destination on a one-to-one basis.
Instead of redirecting all pre-migration content to a single URL, redirect each page one-to-one.
When the page is deleted
Consider redirecting to a new URL if the content you have been managing has been deleted due to a site renewal, etc.
However, there are some caveats when setting up 301 redirects for deleted pages.
Setting up too many 301 redirects on a deleted page can be seen as bad redirects by Google.
There is no problem with redirecting to a few pages, but if it reaches the level of tens or hundreds of pages, you may be penalized by Google, so be careful.
In some cases, instead of setting up a redirect to the deleted page, it may be more useful for users to create a new page to tell them that the content is gone.
Instead of blindly setting redirects, consider what you should do based on the user’s point of view.
When Renewal and Rethinking are Necessary
Redirect processing is also necessary when renewal and URL review are required. A redesign is an overall refinement or improvement of the website, which includes tasks such as introducing a new URL structure and removing outdated content. If it is a small modification, it can be managed on the CMS, but depending on the situation, there may be cases where a lot of modification is required, and redirect processing may be necessary.
By the way, page changes due to renewal can have a big impact on your site’s SEO. Therefore, careful planning and careful testing are critical. Proper implementation of redirects and URL rewriting can help maintain your site’s rankings and improve user experience.
When normalizing the URL
URL normalization is the process of unifying multiple URLs for the same page into one URL and is very important for SEO. URL normalization allows search engines to avoid indexing duplicate content and improve your site’s ranking.
URL normalization does the following:
・Addition/removal of slashes
・Unification of case sensitivity
・Removal of query parameters
・Presence or absence of WWW
The reason URL normalization requires redirects is because there are cases where search engines and users navigate to pages using previous URLs.
If redirects are not set up, search engines will index both the old and new URLs, marking them as duplicate content and lowering your rankings. Also, if the user clicks on the old URL, they may see an error. Therefore, redirect settings are essential when normalizing URLs.
In order to prevent this from happening, it is very important for SEO measures to unify multiple URLs into one URL and make it recognized by Google’s crawler.
If the same content is displayed with different URLs as shown below, be sure to set up a 301 redirect.
・With or without www
・With or without index.html
・http:// and https//
・With or without trailing slashes (http://sample.com/about and http://sample.com/about/)
・When there is a smartphone page with the same content like /sp/
If you do not take any action when renewing your site or relocating your page, your Google search ranking may drop significantly.
In addition to inheriting the content and evaluation of the page before relocation, make sure to set up redirects so that search engines do not recognize that “duplicate content exists”.
Also, when moving, it is necessary to provide support so that users who have accessed it until then will not get lost.
Also Read this Article: What is a redirect? Explain the difference between each redirect and SEO effect
Also read: Free email verifier